Namibia, as a game hunting destination, meets and exceeds the expectations of many international hunting enthusiasts. While many hunters’ expectations of an African destination are quite ordinary, Namibia is one of Africa’s gems that surprises and enthralls visitors to her shores.
[DYNAMIC-BLOGTABLEOFCONTENT]
Why Choose Namibia as a Game Hunting Destination?
- If dangerous game hunting is what you are after, Namibia will not disappoint. All Big 5 and Dangerous 7 members are available when hunting in Namibia.
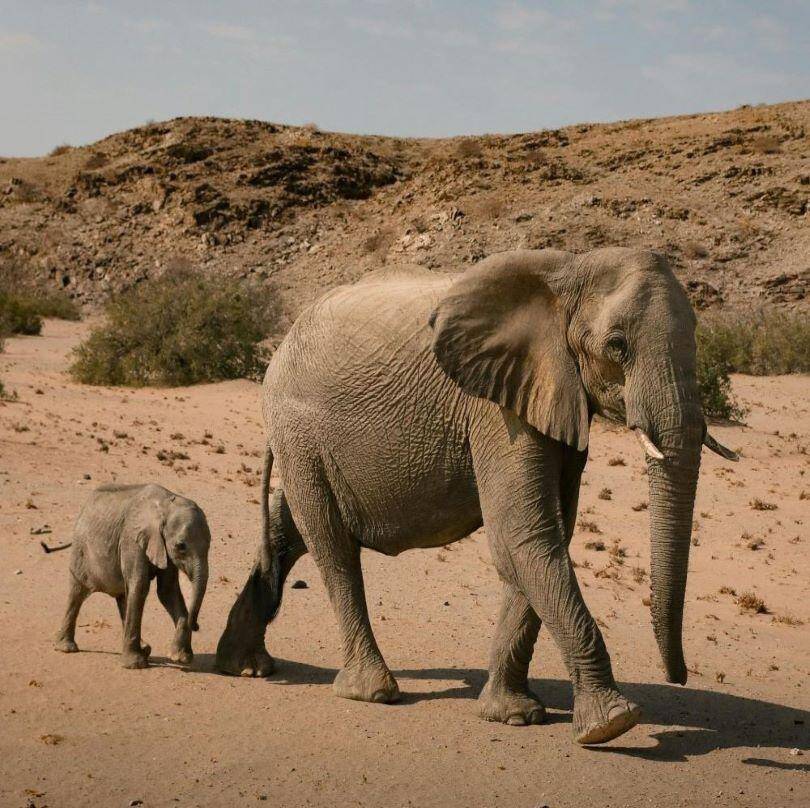
- Elephant hunting in Namibia annually produces exceptional trophies and options for exportable and non-exportable dangerous game hunting trips. It is seen as particularly challenging with large tusks being the ultimate dangerous game hunting trophy.
- Namibia is known worldwide for ethical and sustainable hunting practices.
- Namibia’s climate allows for ideal game hunting conditions, with warm days and cold nights being the order of the day.
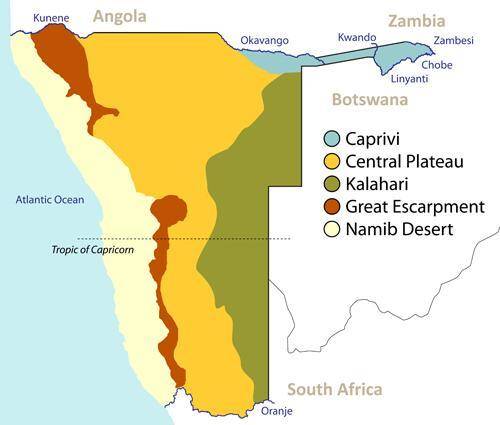
- Seen as a real hunters’ paradise, Namibia’s diverse landscape is divided into five distinct geographical areas, namely the Central Plateau, the Bushveld, the Namib Desert, the Kalahari Desert, and the Great Escarpment, allowing for a variety of conditions to enjoy during the hunting safari.
Namibia As A Tourism Destination
Namibia’s abundant range of landscapes, amazing wildlife, rich heritage, and diverse cultures come together to weave a tapestry of experiences that as a tourist, leaves one wanting more. It is a destination that welcomes one with open arms, to experience her charms as you wish.
Part of this destination’s unique makeup includes its diverse range of wildlife. From minute antelopes such as the Damara Dik-Dik to the large African elephant, the country is thriving with exceptional and varied species.
An online article from the Namibia Economist (9 February 2024) confirmed that Namibia’s tourism industry contributed 6,9% of the country’s GDP in 2022. That equated to an estimated N$14,3 billion!*
2022 saw more than 243, 466 tourists visit the country. Of these, 3,152 were hunters from more than 50 countries worldwide, experiencing what Namibia had to offer and enjoying some fantastic game hunting safaris. And one of the trophies that is extremely popular with these international hunters, is the African elephant.

The African Elephant At a Glance
- There are two types of African elephants, namely the African bush elephant, and the African Forest Elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis).
- The African Bush elephant, also known as the African savannah elephant, is native to areas of sub-Saharan Africa, including Uganda, Kenya, Tanzania, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Namibia, Zambia, South Africa, and Angola.
- The African Forest elephant is native to the humid tropical forests in West Africa and the Congo Basin and is the smallest of the three living elephant species, reaching a shoulder height of 7,8 feet.
- The African bush elephant is the world’s largest land mammal, with a bull topping the scales at around 5,000-14,000 pounds and smaller females weighing 6,000-8,000 pounds.
- Although this herbivore is often referred to as a “gentle giant,” things can change very quickly should the elephant feel threatened or afraid.
- They can become very territorial and aggressive towards real or perceived threats, including humans.
- They can reach speeds of up to 25 miles per hour – keep this in mind if your dangerous game hunting safari goes south since humans run at an average of just over 7 miles per hour…
Where are the Best Locations in Namibia for Elephant Hunts?
Hunters are spoiled for choice in elephant hunting in Namibia, with numerous options available. Two of the most popular options for elephant hunting would be the Zambezi region, formerly known as the Caprivi Strip, and Bushmanland.
Situated in the far northeastern corner of the country, the Zambezi region is known for its lush, green vegetation. Heavy summer rainfalls in the area produce wonderfully inviting vegetation, and the area is swimming with animals, including many dangerous game hunting species such as the hippo, Nile crocodile, Cape buffalo, and elephant.
Bushmanland’e elephants form part of free-range dangerous game hunting safaris. The terrain in the area includes Kalahari sands, woodlands, and flat landscapes.
When we talk about elephant hunts and locations within Namibia, you cannot help but mention the elusive desert-adapted elephant, found in southern Kunene and northern Erongo. Hunting this magnificent beast is rather controversial, but let’s find out more about this fascinating creature.
Namibia’s Desert-Adapted Elephant
While these desert elephants found in the arid and semi-arid regions of Namibia were once thought to be a sub-species of the African elephant, it has instead been confirmed that they are indeed African elephants with special adaptions that have allowed them to live and thrive in such harsh, arid, and seemingly uninhabitable conditions. They have adapted to extreme temperatures and challenging conditions, making the area their home. While somewhat controversial, desert-adapted elephant hunting in Namibia does take place.
The Desert Elephant at a Glance
Location: Riverbeds within Namibia, including the Uniab, Hoarusib, Huab, Hoanib, and Ugab Rivers
Habitat: Arid and semi-arid regions of Namibia, including dry riverbeds, desert, gravel areas and mountainous regions of Namibia
IUCN Classification: Endangered, with a decreasing population
Are Namibia’s Desert Elephants a Sub-Species of the African Elephant?
No, these adaptable desert elephants are in fact, also African elephants that have adapted in various ways to survive the arid, hostile terrain in which they find themselves.
Are Namibia’s Desert Elephants Hunted on Safari?
Yes, they are hunted and it does take place, but this is a rather controversial topic.
While hunting permits for these elephants have been sold, conservationists argue that there are, in fact, fewer desert elephants than were estimated left in the area. While many estimate the number of these desert-dwelling mammals to be more than 150, some argue the numbers are closer to 100. It has been said that there are fewer than 20 elephant bulls, and their loss could potentially have major implications for the livelihood and continuance of the herd.
What kind of Habitat do the Desert-Adapted Elephants live in?
- These desert-adapted elephants live in a harsh environment and certainly not one where you would expect any mammal as large as themselves to satisfactorily live and survive.
- They are found in the arid and semi-arid regions of northwestern Namibia. The regions of southern Kunene as well as the northern Erongo region (formerly called Damaraland) are what these elephants call home.
- The area consists of gravel plains, rocky mountain terrain as well as a large section of desert.
- While the area is dry and receives a negligible rainfall of 2-6 inches annually, the elephants are often found in the dry riverbeds of some of the rivers, including the Huab, Ugab, Hoanib, Hoarusib, and Uniab Rivers.
- These rivers are usually only filled or running after storms, but still provide shelter and food sources for the elephants.
- The elephants dig holes within the riverbeds to find water.
- They use water, sand, dust, and mud to protect their skin from the harsh African sun as well as insects and bugs that bite and sting them.
How have the Desert-Adapted Elephants Adapted to Survive in this Harsh Environment?
It is amazing to think that in one part of Namibia, some African elephants are bathing in a river in the lush Caprivi Strip, while in another, other African elephants are surviving in the desert!
To survive in these harsh conditions, several adaptions have been noted:
- The desert-dwelling elephant can last several days without water. A female elephant and her offspring can manage up to three days without water, while an adult elephant bull can manage up to five days without water.
- Due to the harsh conditions in which they live, these desert-adapted elephants are not as large as their counterparts living in other regions of the country.
- Because they have less body mass, they appear taller and their feet bigger. Their wide feet do, however, assist them when walking across the Namib Desert.
- They can walk and cover large distances to search for food and water.
- They are more active at night and will travel great distances and search for food and water during the cooler evenings.
How do the Desert-Adapted Elephants Survive in terms of Food and Water?
Namibia’s desert-dwelling elephants are truly unique. They feed on a large variety of available foods including grasses, bulbs, fruits, leaves, shoots, and flowers, amongst others. They have seasonal feeding preferences that allow them to utilize the available food sources to their best advantage, for example, should one food source be in abundance during a particular season they will focus on that before focusing on another variety of food.
These mammals can go for days without water, as they eat moisture-laden food in the riverbeds to assist with moisture intake. A female elephant and her young can survive up to three days without water, while an elephant bull can manage up to five days without water.
These elephants are also known to be more active during the nights when it is cooler, rather than moving and roaming during the day in the excessive heat. They can live in any conditions where there is access to sufficient food and water.
Their ability to adapt to their surroundings and available food and water resources has allowed them to adapt to these harsh conditions.
How do Namibia’s Conservation Policies Assist the Desert-Dwelling Elephant?
There have been conservation strategies that have been implemented for the desert-dwelling elephants and these focus on sustainable land management and community-based natural resource management (CBNRM). The Namibian government is extremely proactive when it comes to conservation in the country, something which many other African countries can learn from.
These initiatives include:
- Through CBNRM programs, the local communities play a role in the conservation of the animals, taking into consideration the needs of the people and reaching a situation where both the local communities and the wildlife benefit.
- Local communities are recognized for the role they play in protecting wildlife and are empowered to continue their roles.
- The country itself faces major climate challenges, including water, or the lack thereof. By introducing and implementing conservation efforts, the climatic impacts on elephant habitats may be less, thereby giving them a greater chance of survival in the harsh environment in which these animals find themselves.
- Namibia contributes towards the ecological balance and global diversity by protecting these elephants.
How does Hunting in Namibia assist in Conservation?
Namibia takes conservation very seriously indeed. Since the country gained independence in the 1990s, it has become the first African country to include environmental protection in its constitution. The government has empowered local communities to manage and benefit from wildlife on their lands through communal conservancies.
Namibia practices conservation hunting, which, in essence, refers to hunting that meets specific criteria, The benefits of conservation hunting include:
- The hunting will only take 1% of the national herd.
- Conservation hunting generates over 10 times more income per animal harvested than meat harvesting.
- Meat, however, is provided as a by-product and provides protein for community members.
- Income from hunting supports the community game guards’ salaries.
- Namibia incentivizes communities to safeguard the wildlife on their lands by allowing hunting as sustainable utilization.
- With game hunting activities that are well regulated and generating revenue, conserving wildlife is now seen as an attractive option for local communities, thereby assisting in their conservation.
Elephant Hunting in Namibia: Conservation Remains Key
Elephant hunting in Namibia is still seen by some as being rather controversial, especially when it comes to the desert-adapted elephant. While many may be against elephant hunting, the fact remains that the elephant populations in Namibia are extremely well-managed and protected. Trophy elephant hunting in Namibia allows for revenue to be utilized for conservation efforts.
These members of Africa’s Big 5 and Dangerous 7 are just that – big and dangerous – and at times can cause havoc with crop raiding when food sources are scarce. There has apparently been an increase in human-wildlife conflict involving elephants, such as the desert-dwelling elephants that have occasionally come into conflict with local communities. These “problem” elephants can be disposed of through a dangerous game hunting safari, should a permit be issued.
Elephant hunting in Namibia remains a sought-after dangerous game hunting adventure that many wish to experience, and a person must congratulate the Namibian government and the various role players involved for their balanced approach in the consideration of human safety, economic considerations, as well as conservation.
Author: B. Hershensohnn
